

.
.
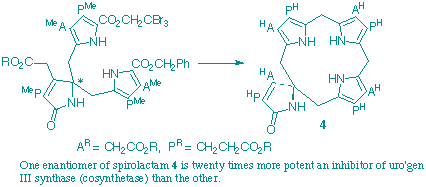 80
80
M. A. Cassidy, N. Crockett, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Biosynthesis of Porphyrins and Related Macrocycles, Part 44. Synthetic and Stereochemical Studies on the Proposed Spiro Intermediate for Biosynthesis of the Natural Porphyrins"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1996, 2079-2090.
Full Text
A route has been devised for synthesis of both enantiomers of the spiro-lactam. The enzyme uroporphyrinogen III synthase (cosynthetase), which converts hydroxymethylbilane into uroporphyrinogen III, is competitively inhibited more than twenty times more strongly by one enantiomer of than by the other. This finding adds further strong support to the view that cosynthetase acts by generating the spiro-pyrrolenine as an intermediate.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 81
81
A. C. Spivey, A. Capretta, C. S. Frampton, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Biosynthesis of Porphyrins and Related Macrocycles, Part 45. Determination of the Absolute Configuration of the Spirolactam which Inhibits Cosynthetase"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1996, 2091-2102.
Full Text
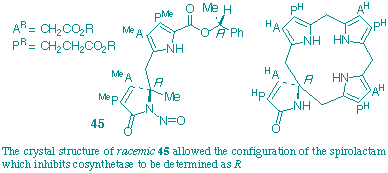
A novel approach, involving X-ray analysis of a specifically designed racemate, in combination with correlations by circular dichroism, has allowed the absolute configuration of the spirolactam to be determined. The outcome is that the enantiomer of this lactam which strongly inhibits uroporphyrinogen III synthase (cosynthetase) has the R-configuration and the implications of this finding are briefly discussed.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 82
82
F. J. Leeper, M. Rock and D. Appleton
"Synthesis of Analogues of Porphobilinogen"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1996, 2633-2642.
Full Text
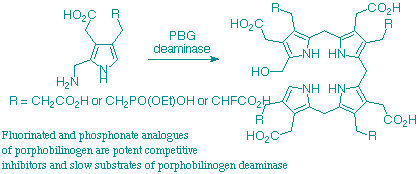
Syntheses are described of several analogues of porphobilinogen intended as substrates and/or inhibitors of porphobilinogen deaminase (hydroxymethylbilane synthase). 2-Methylporphobilinogen was synthesised from 2-methylpyrrole, whereas a phosphonate analogue of porphobilinogen, 8,9-dehydroporphobilinogen and 9-fluoroporphobilinogen were all made from the azaindole. The best route to avoided fluoroacrylate because of loss of fluorine during reduction of the double bond.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 83
83
F. J. Leeper and M. Rock
"Interaction of Analogues of Porphobilinogen with Porphobilinogen Deaminase"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1996, 2643-2649.
Full Text
2-Methylporphobilinogen and 8,9-dehydroporphobilinogen are only weak inhibitors of porphobilinogen deaminase (hydroxymethylbilane synthase). The phosphonate analogue and 9-fluoroporphobilinogen are good inhibitors, however, and also act as slow substrates (the first unnatural substrates known for this enzyme). The particularly strong inhibition shown by the fluoro analogue is shown to be due to the slow regeneration of free enzyme once the compound has become covalently bound to it. This results in a sigmoidal dependence of rate vs. [substrate].
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 84
84
D. Appleton and F. J. Leeper
"Deuterium Isotope Effects on Porphobilinogen Synthesis Catalysed by 5-Aminolaevulinic Acid Dehydratase"
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.,1996, 6, 1191-1194.
Full Text
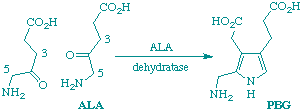
Deuteriation of 5-aminolaevulinic acid (ALA) at C-5 has no effect on the rate of porphobilinogen synthesis by ALA dehydratase from Bacillus subtilis but deuteriation at C-3 gave isotope effects on kcat and kcat/KM of 3.4 and 2.3 respectively. Reisolated ALA after 50% reaction shows no significant loss of deuterium at C-3, indicating that it is probably the first deprotonation at this carbon which is rate-determining.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 85
85
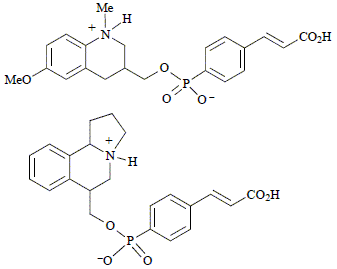
C. Gonzalez Bello, C. Abell and F. J. Leeper
"Synthesis of tetrahydroquinolines, hexahydrobenzoindolizines and an aryl phosphonate linker for the generation of catalytic antibodies"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1997, 1017-1024.
Full Text
Syntheses of 6-methoxy-1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-3-methanol and 1,2,3,5,6,10b-hexahydrobenzo[g]indolizine-6-methanol are described. The aryl phosphonic acid, which can be used as a linker to a protein, is synthesised and coupled to the above alcohols. These haptens, when linked to a protein, are intended to generate antibodies able to catalyse cationic cyclisation reactions.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 86
86
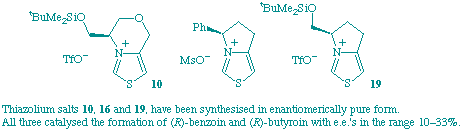
R. L. Knight and F. J. Leeper
"Synthesis of and Asymmetric Induction by Chiral Bicyclic Thiazolium Salts"
Tetrahedron Lett.,1997, 38, 3611-3614.
Full Text
Three different chiral bicyclic thiazolium salts have been synthesised in enantiomerically pure form. These salts all catalysed the formation of benzoin and butyroin from benzaldehyde and butyraldehyde respectively and the product had the R-configuration in each case with e.e.'s in the range 10-33%. Possible reasons for these results are discussed.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 87
87
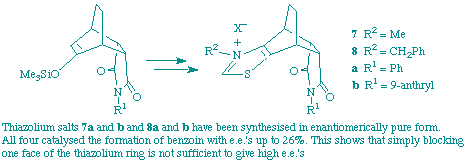
A. U. Gerhard and F. J. Leeper
"Synthesis of and Asymmetric Induction by Chiral Polycyclic Thiazolium Salts"
Tetrahedron Lett.,1997, 38, 3615-3618.
Full Text
Polycyclic thiazoles have been synthesised and the enantiomers resolved. Alkylation gave chiral thiazolium salts which catalyse the dimerisation of benzaldehyde to give benzoin with enantiomeric excesses up to 26%. Reasons for these results are discussed.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 88
88
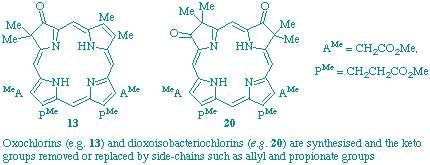
J. J. De Voss, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Synthetic studies relevant to biosynthetic research on vitamin B12. Part 12. Modification of the periphery of chlorins and isobacteriochlorins"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1997, 1105-1116.
Full Text
Oxochlorins and dioxoisobacteriochlorins, which can be prepared from readily synthesised porphyrins, have been used as starting materials to develop mild, efficient methods (a) for reductive removal of the oxo-functionality to yield chlorins and isobacteriochlorins and (b) for attachment of an allyl substituent at the macrocyclic carbon bearing the oxo-functionality. It has been demonstrated that the allyl group can act as a precursor of a propionate residue, a group commonly present in the natural porphinoids.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 89
89
C. J. Aucken, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Haem d1: Stereoselective synthesis of the reduced form of its parent macrocycle using the original coupling strategy"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1997, 2099-2109.
Full Text
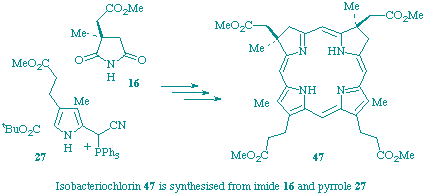
A substituted isobacteriochlorin, which corresponds structurally to the reduced metal-free macrocycle of haem d1, has been synthesised by a stereoselective route in which the final step is a photochemical 18-pi-electron antarafacial cyclisation of an open-chain precursor.
.
.
.
.
--- Next ten abstracts ----- Previous ten abstracts ---