

.
.
.
.
.
30
The isolation and characterization of polivione, a polyketide metabolite and probably a precursor of
citromycetin (1), from Penicillium frequentans is reported. The structure elucidation of polivione is based on a detailed study of its high-field 1H and 13C n.m.r. spectra. Extensive use was made of two-dimensional homonuclear and heteronuclear correlation experiments in the assignment of the n.m.r.
spectra. Some chemical transformations were also explored, both to confirm its structure and to
investigate its relationship to citromycetin.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
31
Syntheses are described of two compounds having the 1,4-(propane-1,3-diyl)tripyrrin macrocycle (5),
which is the basis of the spiro compound (2) proposed as an intermediate during the cyclization of
hydroxymethylbilane (1) to uro’gen Ill (3), catalysed by the enzyme cosynthetase. The first synthesis, of
the dinitrile (41), starts with the alkylation of malononitrile with two different chloromethylpyrroles,
whereas the second synthesis, of the spiro lactam (59) uses the condensation of nitroalkanes with
pyrrole aldehydes. In both cases the macrocycle is completed by addition of a third pyrrole ring followed
by acid-catalysed cyclization from an a-free pyrrole onto a hydroxymethyl substituent. The crystal
structure of the dinitrile (41) shows a rigid, highly puckered macrocycle and the same conformation in
the spiro lactam (59) is used to explain the existence of two non-interconvertible isomers, (61) and (62).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
32
The 12-methyl analogue (13) of the aromatised form of precorrin-3 (5) has been prepared by enzymic C-methylation
of 12-decarboxy-uro’gen-Ill (2) and is used for incorporation experiments which indicate that decarboxylation of the
12-acetate residue in B12-biosynthesis occurs after C-17 methylation.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
33
lsobacteriochlorins carrying a C-methyl group at C-20 of the macrocycle are important for research on
the biosynthesis of vitamin B12. Several different approaches are studied which allow the introduction of
a C-20 methyl group into model isobacteriochlorins, the most successful involving the stepwise
reduction of a nitrile residue to a methyl group. Successful syntheses are described of two 20-
methylisobacteriochlorins and two 20-cyanoisobacteriochlorins. All the routes used depend finally on the
photochemical cyclisation of an 18p-electron open-chain precursor.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
34
Biosynthesis of the organic nuclei of hemes, chlorophylls, cytochromes, andvitamin B12 involves, as a first stage, the building of a linear tetrapyrrole by the enzyme hydroxymethylbilane synthase. This enzyme has been found to use a novel dipyrrolic cofactor whose structure has been established. The function of this cofactor in the building process and the way in which the cofactor is bound to the enzyme have both been determined.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
35
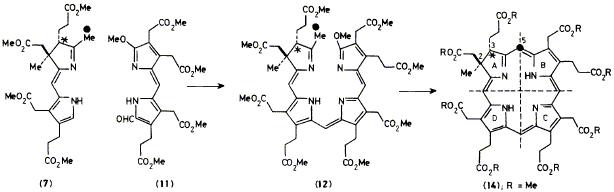
(+)-[5-13C]Faktor-l ester is synthesised following an east-west disconnection strategy and is used to show by
specific enzymic incorporation experiments that the first C-methylation product, precorrin-1, on the B12-biosynthetic
pathway is a tetrahydrochlorin.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
36
Reviewing the literature published during 1986 and 1987.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
37
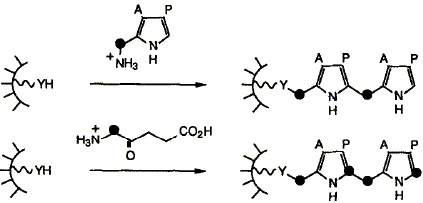
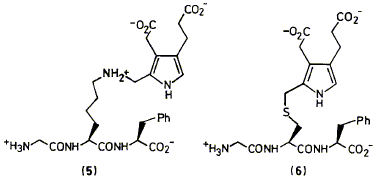
Syntheses are described of two compounds having a pyrrolylmethyl group attached respectively to
the sulphur of cysteine (6) and the e-nitrogen of lysine (5). These compounds were built to act as
model systems for two possible ways in which pyrrolylmethyl groups could be bound to the protein
of the enzyme hydroxymethylbilane synthase (HMBS), also known as porphobilinogen deaminase.
We show how results from these studies were important in the discovery and characterisation of
the novel pyrromethane cofactor (4) of HMBS.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
38
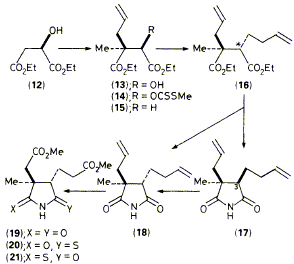
An efficient enantioselective synthesis of (-)-ring-B imide (19) from R-malic acid is outlined and this product is used
for synthesis, by a photochemical route, of the 2,7,20-trimethylisobacteriochlorin (3), of importance for biosynthetic
research on vitamin B12.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
39
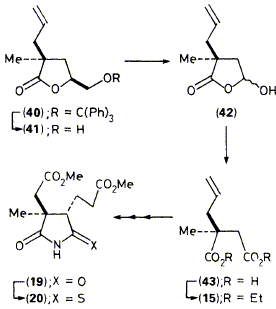
An enantioselective synthesis of (-)-ring-B imide (19) from inexpensive glutamic acid is described and the product is used for synthesis of the 2,7,12,20-tetramethylisobacteriochlorin (39) required for future transformation into later biosynthetic intermediates for vitamin B12.
.
.
.
.
.
--- Previous ten abstracts ------ Next ten abstracts ---
.
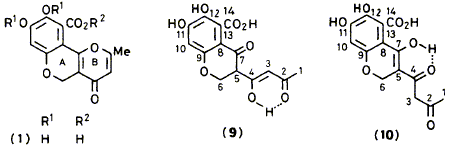
A. K. Demetriadou, E. D. Laue, F. J. Leeper and J. Staunton
"Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Polivione, a Polyketide Co-metabolite of Citromycetin in Penicillium frequentans"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1988, 763-768.
Full Text
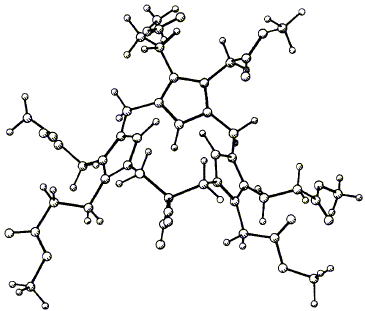
W. M. Stark, M. G. Baker, F. J. Leeper, P. R. Raithby and A. R. Battersby
"Biosynthesis of Porphyrins and Related Macrocycles, Part 30. Synthesis of the Macrocycle of the Spiro System Proposed as an Intermediate Generated by Cosynthetase"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1988, 1187-1201.
Full Text
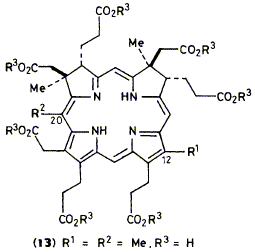
F. Blanche, S. Handa, D. Thibaut, C. L. Gibson, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Biosynthesis of Vitamin B12: When is the 12b-Methyl Group of the Vitamin Generated by Acetate Decarboxylation?"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1988, 1117-1119.
Full Text
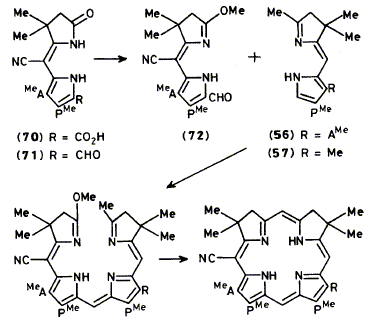
D. M. Arnott, P. J. Harrison, G. B. Henderson, Z.-C. Sheng, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Synthetic Studies Relevant to Research on Vitamin B12, Part 9. Synthesis of 20-Methyl and 20-Cyano Isobacteriochlorins"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1989, 265-278.
Full Text
P. R. Alefounder, G. J. Hart, A. D. Miller, U. Beifuss, C. Abell, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Biosynthesis of the Pigments of Life: Structure and Mode of Action of a Novel Enzymatic Cofactor"
Bioorg. Chem.,1989, 17, 121-129.
Full Text
R. D. Brunt, F. J. Leeper, I. Grgurina and A. R. Battersby
"Biosynthesis of Vitamin B12: Synthesis of (±)-[5-13C]Faktor-1 Ester: Determination of the Oxidation State of Precorrin-1"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1989, 428-431.
Full Text
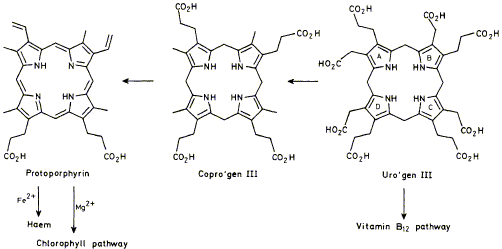
F. J. Leeper
"The Biosynthesis of Porphyrins, Chlorophylls, and Vitamin B12"
Natural Products Reports,1989, 6, 171-203.
Full Text
A. D. Miller, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Biosynthesis of Porphyrins and Related Macrocycles, Part 34. Synthesis and Properties of S-Pyrrolylmethylcysteinyl and e-N-Pyrrolylmethyl-lysyl Peptides"
J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1,1989, 1943-1956.
Full Text
W. G. Whittingham, M. K. Ellis, P. Guerry, G. B. Henderson, B. Muller, D. A. Taylor, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Syntheses Relevant to Vitamin B12 Biosynthesis: The Malate Route to (-)-Ring-B Imide and Synthesis of the 2,7,20-Trimethylisobacteriochlorin"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1989, 1116-1119.
Full Text
B. Muller, A. N. Collins, M. K. Ellis, W. G. Whittingham, F. J. Leeper and A. R. Battersby
"Syntheses Relevant to Vitamin B12 Biosynthesis: The Glutamate Route to (-)-Ring-B Imide and Synthesis of the 2,7,12,20-Tetramethylisobacteriochlorin"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1989, 1119-1122.
Full Text