

01 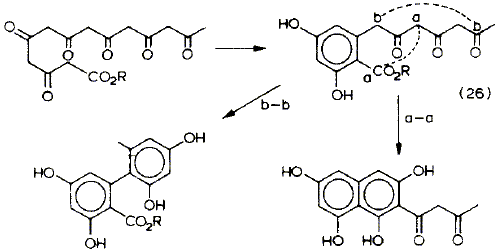 G. E. Evans, M. J. Garson, D. A. Griffin, F. J. Leeper and J. Staunton
G. E. Evans, M. J. Garson, D. A. Griffin, F. J. Leeper and J. Staunton
"Biomimetic Syntheses of Phenols from Polyketones"
in Further Perspectives in Organic Chemistry, 1978, Elsevier, Amsterdam, p. 138.
Full Text
Following speculation that many enzymes exercise control over polyketone cyclisations in vivo by converting a key carbonyl group to a cis-enol ether derivative, two novel biomimetic cyclisations are described. The first involves condensation of two C6 units derived from triacetic lactone to form an aryl pyrone related to aloenin. In the second a nathpopyrone of the rubrofusarin type is formed by condensation of an orsellinic acid derivative with the enol ether of triacetic lactone.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
02 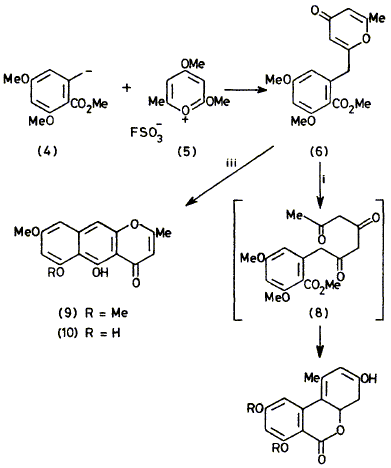
F. J. Leeper and J. Staunton
"Biomimetic Syntheses of Heptaketide Metabolites: Alternariol and a Derivative of Rubrofusarin"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1978, 406-407.
Full Text
Biogenetically inspired syntheses of alternariol and a methyl ether of rubrofusarin are described.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
03 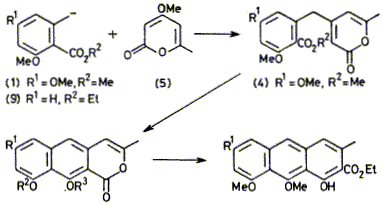
G. E. Evans, F. J. Leeper, J. A. Murphy and J. Staunton
"Triacetic Lactone as a Polyketide Synthon: Syntheses of Toralactone and Polyketide-type Anthracene Derivatives"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1979, 205-206.
Full Text
Condensation of orsellinic and 6-methylsalicylic acid derivatives with triacetic acid lactone methyl ether gives naphthopyrones related to toralactone which can be converted in turn into polyketide-type anthracenes.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
04 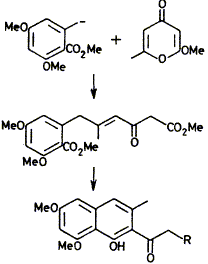
F. J. Leeper and J. Staunton
"Triacetic Lactone and 2,6-Dimethyl-g-pyrone as Polyketide Synthons: Syntheses of Torachrysone and Eleutherinol Derivatives"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1979, 206-207.
Abstract,
Full Text
Derivatives of torachrysone and eleutherinol have been made by reaction of a carbanion of an orsellinic acid derivative with g-pyrones.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
05 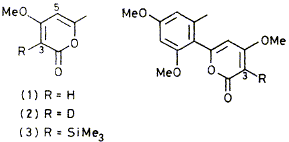
T. A. Carpenter, P. J. Jenner, F. J. Leeper and J. Staunton
"A Novel Kinetic Deprotonation at a Vinylic Carbon in a Pyrone Ring"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1980, 1227.
Full Text
Treatment of 4-methoxy-a-pyrones with butyllithium or lithium di-isopropylaniide causes rapid deprotonation at C(3) of the pyrone ring to give nioderately stable vinylic carbanions.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
06 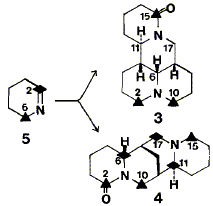
F. J. Leeper, G. Grue-Sorensen and I. D. Spenser
"Biosynthesis of the Quinolizidine Alkaloids. Incorporation of D1-Piperideine into Matrine"
Canad. J. Chem., 1981, 59, 106-115.
Full Text
Label from [6-14C]-D1-piperideineis incorporated nonrandomly into the carbon skeleton of the quinolizidine alkaloid, matrine, in Sophora tetraptera and S. microphylla. The distribution of radioactivity was determined by a new chemical degradation sequence. On the basis of the results, one of two previously postulated biogenetic schemes must be discarded. A modified biogenetic scheme is presented which is consistent with the present results and also leads to the correct stereochemistry of matrine.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
07 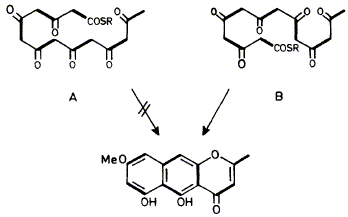
F. J. Leeper and J. Staunton
"Rubrofusarin Biosynthesis in Fusarium culmorum: Incorporation of 13CH313CO2H and CD313CO2H into the Polyketide Naphthalene Nucleus"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1982, 911-912.
Full Text
The pattern of chain-folding in the linear polyketide precursor of the naphthalene nucleus of rubrofusarin has been determined by the standard technique using 13CH313CO2H and by the b-shift technique using CD313CO2H.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
08 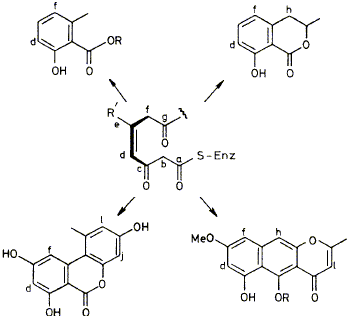
C. Abell, M. J. Garson, F. J. Leeper and J. Staunton
"Biosynthesis of Fungal Metabolites, Alternariol, Mellein, Rubrofusarin and 6-Methylsalicylic Acid from CD3CO2H"
J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun.,1982, 1011-1013.
Full Text
The pattern of incorporation of deuterium from CD3CO2H into the fungal metabolites alternariol, mellein, rubrofusarin, and 6-methylsalicylic acid has been determined by 2H n.m.r. spectroscopy; the results are interpreted in terms of a proposed mode of action for polyketide synthases.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
09 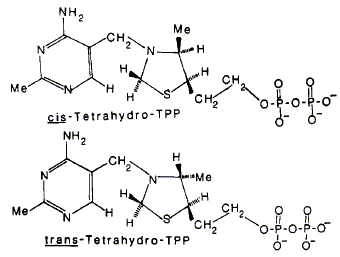
P. N. Lowe, F. J. Leeper and R. N. Perham
"Stereoisomers of Tetrahydrothiamin Pyrophosphate, Potent Inhibitors of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Multienzyme Complex from Escherichia coli"
Biochemistry, 1983, 22, 150-157.
Full Text
Tetrahydrothiamin pyrophosphate, an analogue of thiamin pyrophosphate (TPP) in which the thiazolium ring has been reduced to a thiazolidine ring, was prepared by borohydride reduction of TPP. It consists of four stereoisomers, comprising two diastereomers each of which is a racemic mixture, generated by the introduction of two chiral centers on the thiazolidine ring. The major and minor diastereomers were separated and inferred to be of the cis and trans configurations, respectively, from a study of the nuclear Overhauser effects in the 'H NMR spectrum of the simpler tetrahydrothiamin. Tetrahydro-TPP behaves as a mixture of potent inhibitors of the pyruvate decarboxylase (El) component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Escherichia coli. The site of binding is probably the TPP-binding site on El, and the Kd for each of the four stereoisomers was estimated. The cis isomers of tetrahydro-TPP bind more tightly than does TPP, whereas the trans isomers appear to bind with about the same Kd as TPP. Sodium borohydride caused a rapid inhibition of El activity in the presence of TPP, believed to be due to reaction of borohydride with enzyme-bound TPP. The experiments are consistent with an enhancement of the reactivity of the thiazole ring of TPP when bound to the catalytic site of El, which could be due to polarization of the +N=C bond near a hydrophobic or positively charged region of the protein. A spontaneous reactivation occurred after the initial inhibition by borohydride, attributable to a weakly binding inhibitor, not tetrahydro-TPP, being formed at the catalytic site.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
------ Next ten abstracts ------
.